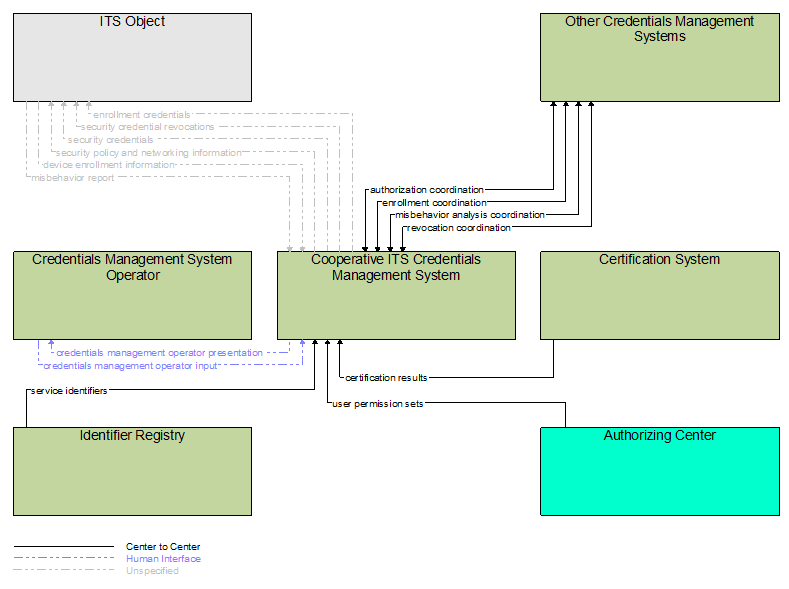
Kind: Subsystem
Class: Support
Type: System
Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System
- Overview
- Functionality
- Triples
- Security
- Interfaces Diagram
- Standards
- Design Details
- Enterprise Concerns
Overview
The 'Cooperative ITS Credentials Management System' (CCMS) is a high-level aggregate representation of the interconnected systems that enable trusted communications between mobile devices and other mobile devices, roadside devices, and centers and protect data they handle from unauthorized access. Representing the different interconnected systems that make up a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), this physical object represents an end user view of the credentials management system with focus on the exchanges between the CCMS and user devices that support the secure distribution, use, and revocation of trust credentials.
As the CCMS interacts with mobile devices and other devices in the Connected Vehicle (CV) environment, these devices pass through stages as certificates and cryptographic material are furnished that enable the device to have trusted interactions with other devices in the CV environment. A simplified version of the device security life cycle is depicted in the following figure.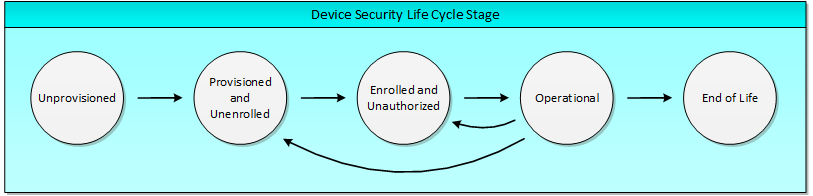
Unprovisioned: The device does not have any of the crypto material or certificates necessary to interact with any parts of the CCMS other than the Provisioning components. Since the end entity is not part of the C-ITS at this stage, it cannot interact in trustworthy fashion with other end entities.
Provisioned and Unenrolled: The device has the crypto material and root certificates necessary to communicate with Enrollment components. At this stage the end entity is still not part of the C-ITS and cannot in trustworthy fashion interact with other end entities.
Enrolled and Unauthorized: The device has all the material it needs to communicate with Authorization components. It still cannot interact with other end entities in trustworthy fashion.
Operational: The device has all the material it needs to communicate with the Misbehavior components, Revocation components, and other operational end entities.
End-of-Life: The device is unable to communicate with any component of the CCMS or other end entities.
This physical object is included in the following Service Packages:
Functionality
| Functional Object |
|---|
| CCMS Authorization |
| CCMS Enrollment |
| CCMS Misbehavior Reporting and Action |
| CCMS Provisioning |
| CCMS Revocation |
Triples
Security
This physical object has the following security levels for the associated service packages.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Security Class | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Service Package |
| Class 5 | High | High | High | Device Certification and Enrollment |
| Class 5 | High | High | High | Security and Credentials Management |
| Class 4 | High | High | Moderate | Core Authorization |
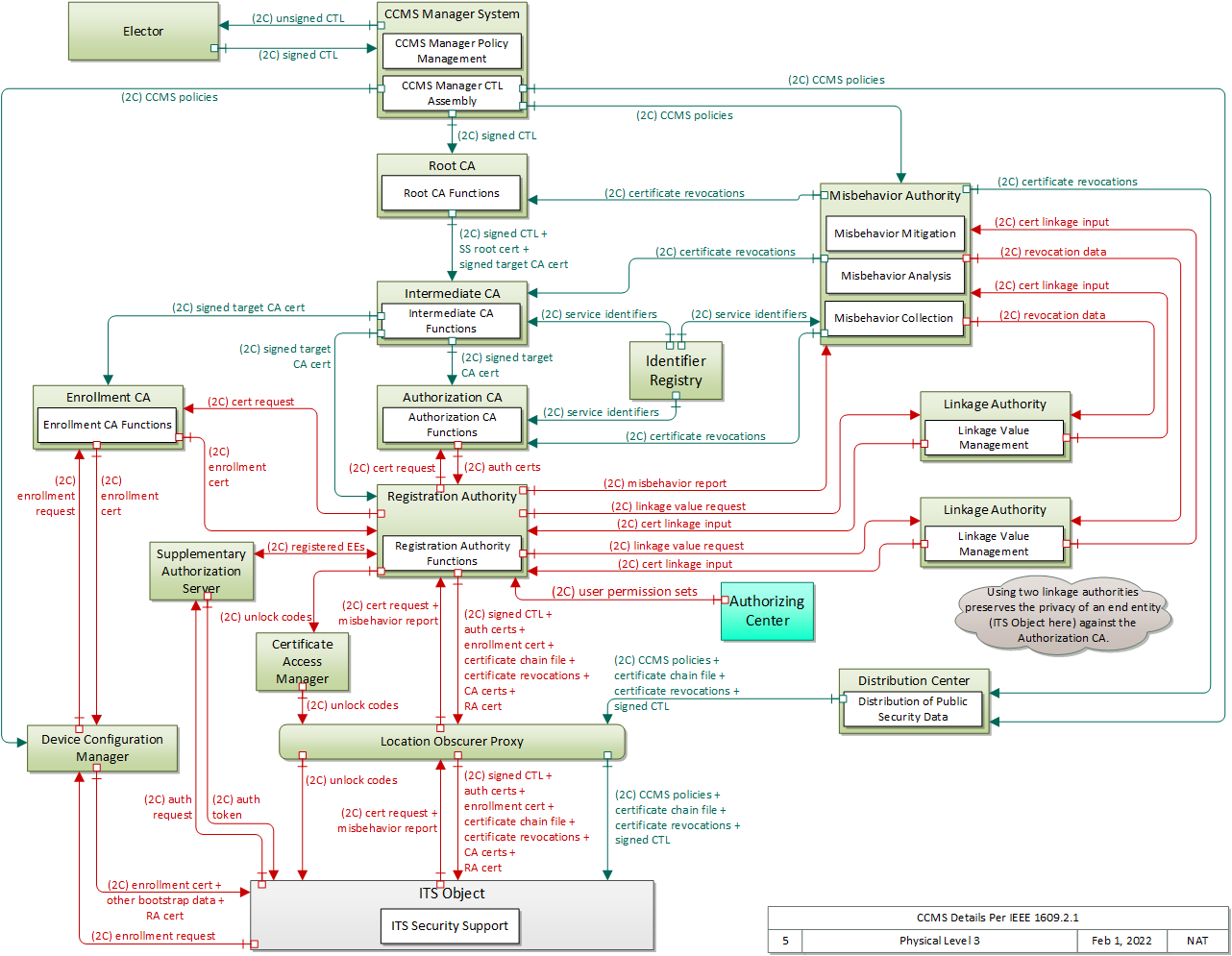
Interfaces Diagram
Standards
Currently, there are no standards associated with the physical object itself though the interfaces may have standards associated with them. For standards related to interfaces, see the specific information flow triple pages.
CCMS Physical Design Details
The physical diagram can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is SVG.SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
In fact, these components must be operated by different enterprises to maintain the checks and balances that are critical to security.
Enterprise Concerns
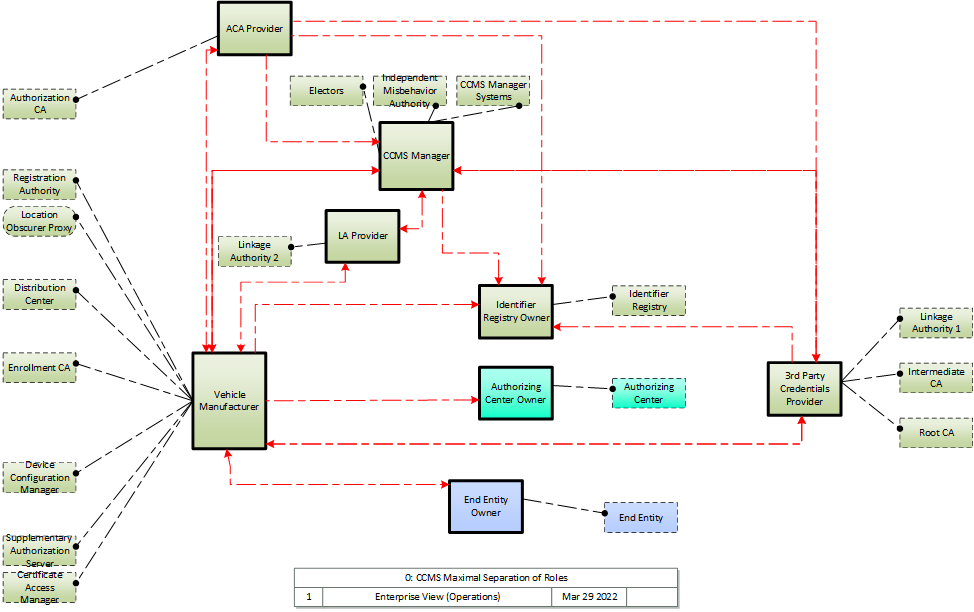
Enterprise concerns related to operation of the C-ITS Credentials Management System are heavily focused on who owns/operates what parts of the CCMS infrastructure. While a viable CCMS can be operated by a single party, the nominal baseline suggests a minimum of two entities: an overarching policy management entity, identified in ARC-IT as the CCMS Manager, that manages the top level of the trust chain, and the entity or entities that provide the remaining bulk of CCMS functionality. Many variations could exist, including but not limited to scenarios where each deployer of end entities (EE) owns and operates their own complete trust chain up to their own root CA, to distributed ownership where key components are owned and operated by distinct entities so as to limit the exposure of end entities to insider attacks. Per IEEE 1609.2.1, this suggest that four different entities own and operate the two linkage authorities, registration authority and authorization CA. Three scenarios illustrating the minimal and maximal, as well as an intermediate approach are illustrated here.
In all scenarios there are distinct parties that own/operate the end entity, authorizing center and identifier registry. The CCMS Manager operates all CCMS Manager systems and electors as well as the misbehavior authority. Certainly the operation of electors and the MA could be further distributed, but these diagrams do not show that. These diagrams also consider only the case where the end entity is a vehicle, and so its manufacturer is the provider of credentials at least to some degree. If the end entity is a roadside unit, 'vehicle manufacturer' would be replaced with the RSU manufacturer or 3rd party that provides credentials for the RSU.
1. Consolidated Roles -- In this scenario the Vehicle Manufacturer (or other device manufacturer) is responsible for the bulk of the trust chain. While this could be implemented by a 3rd party, the point of this scenario is that the provider of the device is the provider of the entire credentialing trust chain.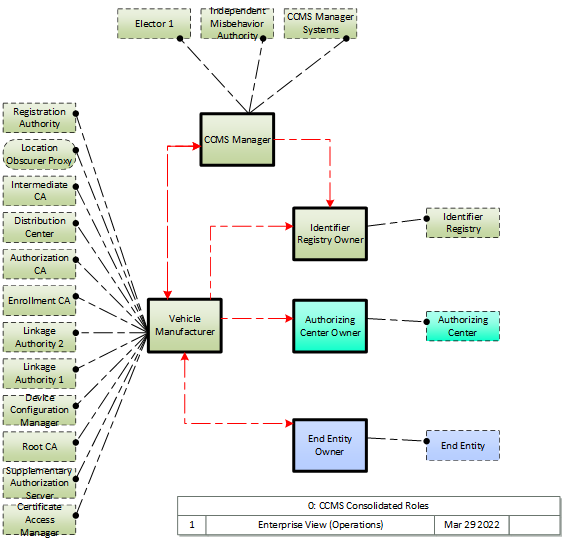
2. Some Separation of Roles -- In this scenario a 3rd party owns part of the traditional trust chain -- the Root CA and Intermediate CA, as well as one of the linkage authorities; the Vehicle Manufacturer (or other device manufacturer) is responsible for the balance of the trust chain. 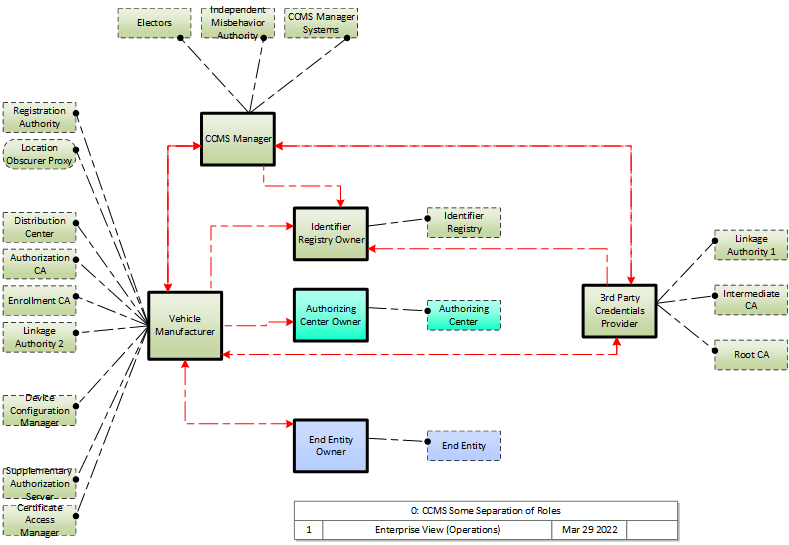
3. Maximal Separation of Roles -- In this scenario:
- one 3rd party owns the Root CA, Intermediate CA and one linkage authority
- another 3rd party owns the Authorization CA
- another 3rd party owns the second linkage authority
- the Vehicle Manufacturer owns the Enrollment CA, Registration Authority and the other vehicle-facing systems
This scenario is maximally protective of End Entity privacy, as the two linkage authorities, registration authority and authorization certificate authority have separate ownership.