Congestion Management Process
A congestion management process (CMP) is a systematic approach for managing congestion that provides accurate, up-to-date information on transportation system performance and assesses alternative strategies for congestion management that meet state and local needs. As defined in 23 CFR 450, the CMP is intended to serve as a systematic process that provides for safe and effective integrated management and operation of the multimodal transportation system. A CMP is required for all designated Transportation Management Areas (TMAs). The process, as defined in the
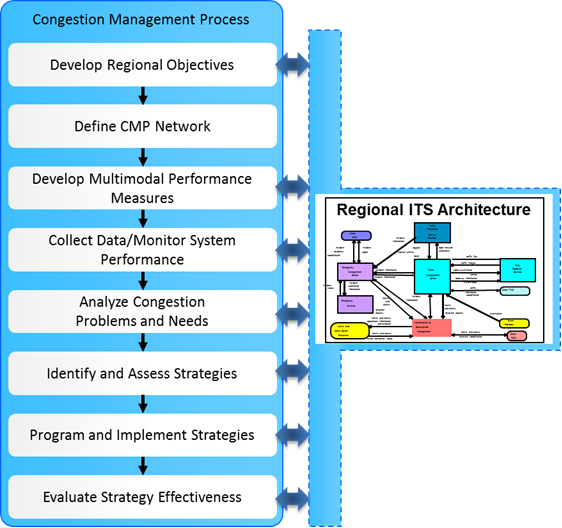
FHWA Congestion Management Process Guidebook, includes the eight steps identified in the figure.
Architecture and Standard Use
The architecture is used in the CMP much as it is used in other systematic transportation planning processes. As shown in the figure, it supports each of the steps except for the definition of the CMP network. Congestion management objectives should be mapped to the regional ITS architecture using RAD-IT. This links the architecture with the CMP and harnesses the traceability built into the architecture to support the remaining CMP steps. The CMP focuses on performance measurement and monitoring. These steps are well supported in the architecture, which identifies operational data sources and interfaces that support performance monitoring. Data collection and monitoring projects can also be included in the project sequencing of the regional architecture. Like the objectives, the congestion management strategies that are identified can be entered on the RAD-IT planning tab and related to the services – the service packages – in the regional ITS architecture. The list of service packages in the architecture can also provide a menu of strategies. Service packages that are related to the selected congestion management strategies can be further refined and defined as ITS projects in the regional architecture project sequencing.
